1.1 Definition & Importance of Automation
What is Industrial Automation?
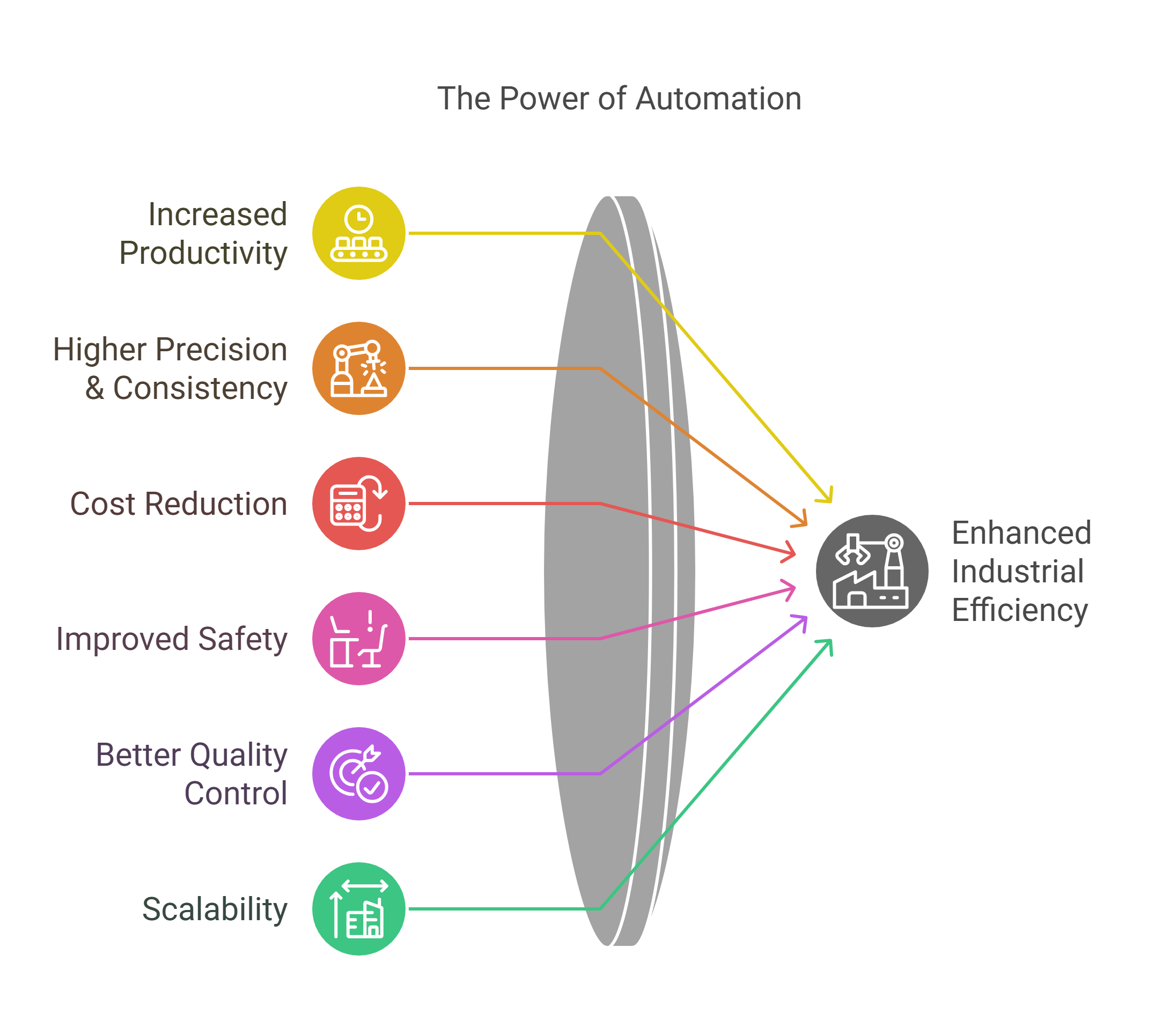
Industrial automation refers to the use of control systems, such as computers, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and robotics, to manage industrial processes with minimal human intervention. It enhances efficiency, precision, and productivity in manufacturing and production industries.
Importance of Industrial Automation
1.2 Types of Automation Systems
There are three main types of automation systems used in industries:
1. Fixed Automation (Hard Automation)
Designed for high-volume production with a dedicated system performing repetitive tasks.
Example: Automotive assembly lines, bottling plants, and textile manufacturing.
Advantages: High production rates, low unit cost.
Disadvantages: Inflexible, expensive to modify for new products.
2. Programmable Automation
Involves systems that can be reprogrammed to handle different tasks based on production needs.
Example: CNC machines, PLC-based assembly lines, and robotic welding systems.
Advantages: Flexible, cost-effective for batch production.
Disadvantages: Slower than fixed automation, requires programming expertise.
3. Flexible Automation
Advanced automation systems that can handle multiple tasks with minimal reprogramming.
Example: Industrial robots, smart manufacturing systems, automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Advantages: High adaptability, suitable for mass customization.
Disadvantages: High initial investment, complex integration.
1.3 Real-World Applications in Manufacturing & Industry
1. Automotive Industry
Example: Automated robotic arms in car assembly lines for welding, painting, and part installation.
Benefits: Increased precision, faster production, improved safety for workers.
2. Food & Beverage Industry
Example: Automated packaging systems, robotic food sorting, quality control sensors.
Benefits: Consistency in packaging, faster production speeds, compliance with hygiene standards.
3. Electronics Manufacturing
Example: Automated soldering machines, pick-and-place robots for assembling circuit boards.
Benefits: Reduced human errors, miniaturization of components, high-speed production.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry
Example: Automated drug formulation, packaging, and quality control inspections.
Benefits: Precision in dosage, compliance with stringent health regulations, higher production efficiency.
5. Oil & Gas Industry
Example: Remote monitoring and control of pipelines, automated drilling equipment.
Benefits: Reduced risks in hazardous environments, increased operational efficiency.
6. Smart Factories (Industry 4.0)
Example: AI-driven predictive maintenance, IoT-enabled production monitoring.
Benefits: Real-time data analysis, reduced downtime, adaptive manufacturing.
Conclusion
Industrial automation is revolutionizing various industries by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing safety. Understanding different automation systems and their real-world applications is essential for engineers, technicians, and business owners looking to implement automation in their operations.
In the next chapter, we will explore the Basics of Electrical Components in Automation, which play a crucial role in the automation process.